Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne viral disease that has rapidly spread across the world in recent decades. It is a severe health concern affecting millions of people annually. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 390 million dengue infections occur globally each year, with about 96 million resulting in illness. Understanding dengue fever is crucial for prevention and management, especially in tropical and subtropical regions where the disease is most prevalent.
As the world becomes more interconnected, the risk of dengue fever spreading to new areas increases. This has made it imperative for individuals, communities, and governments to take proactive measures to combat the disease. Early detection and proper management can significantly reduce the mortality rate associated with dengue fever.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of dengue fever. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a concerned individual, or someone interested in learning more about this global health issue, this article aims to provide you with all the information you need to stay informed and protected.
Read also:Billy Harris The Remarkable Journey Of A Visionary In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Dengue Fever
- What Causes Dengue Fever?
- Recognizing the Symptoms of Dengue Fever
- How is Dengue Fever Diagnosed?
- Treating Dengue Fever: What You Need to Know
- Preventing Dengue Fever: Effective Strategies
- Global Statistics and Trends
- The Role of Vaccines in Fighting Dengue
- The Impact of Dengue Fever on Public Health
- Future Directions in Dengue Research
Introduction to Dengue Fever
What is Dengue Fever?
Dengue fever is a viral disease transmitted primarily by the Aedes aegypti mosquito. It is caused by one of four closely related dengue viruses (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4). While most cases result in mild symptoms, some can progress to severe dengue, which can be life-threatening without proper treatment.
The disease is endemic in over 100 countries, with the highest incidence in Southeast Asia, the Western Pacific, and the Americas. Despite significant efforts to control its spread, dengue fever remains a major public health challenge, particularly in urban and semi-urban areas.
Why is Dengue Fever a Global Concern?
The increasing urbanization and globalization have contributed to the spread of dengue fever. Mosquitoes that carry the virus thrive in environments with stagnant water, making densely populated cities with poor sanitation ideal breeding grounds. Climate change has also expanded the geographical range of these mosquitoes, further complicating efforts to control the disease.
What Causes Dengue Fever?
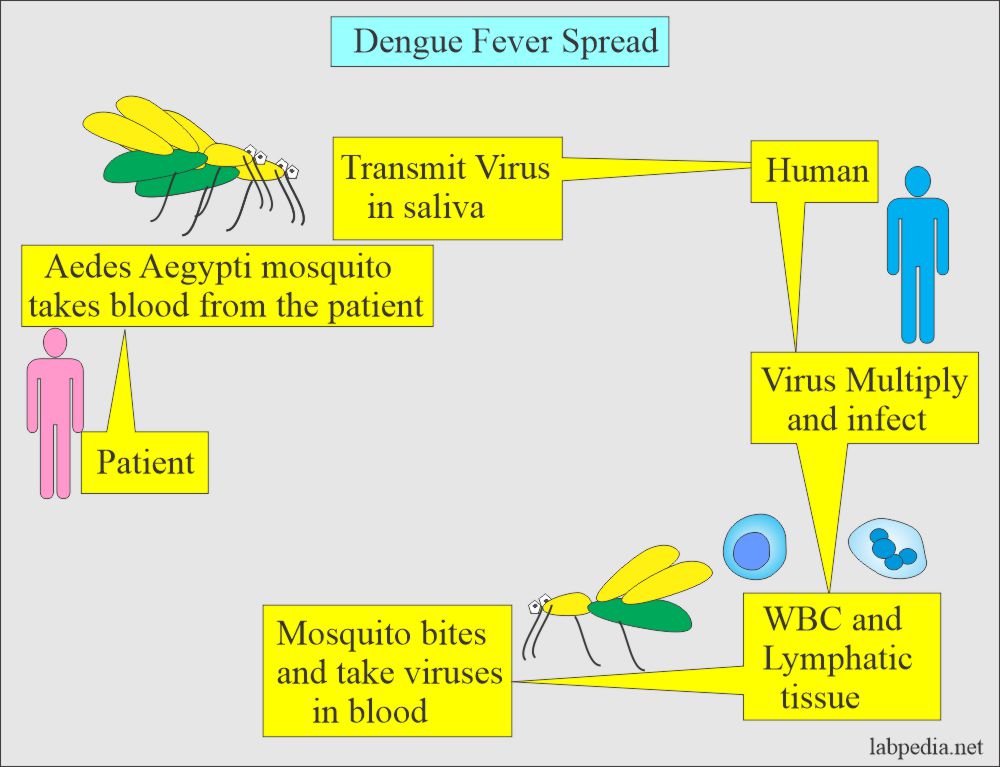
Dengue fever is caused by the dengue virus, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected female Aedes mosquitoes. These mosquitoes typically bite during the day, with peak activity in the early morning and late afternoon.
Transmission Cycle
- Aedes mosquitoes become infected when they feed on a person already infected with the dengue virus.
- After an incubation period of about 8-10 days, the mosquito can transmit the virus to other people through subsequent bites.
- Humans are the primary host of the virus, and there is no evidence of direct transmission between people.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Dengue Fever
The symptoms of dengue fever typically appear 4-10 days after infection and can range from mild to severe. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial for timely treatment.
Common Symptoms
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Pain behind the eyes
- Muscle and joint pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rash
In severe cases, dengue fever can progress to dengue hemorrhagic fever (DHF) or dengue shock syndrome (DSS), which are characterized by bleeding, plasma leakage, and shock.
Read also:Minneapolis Weather A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding The Climate And Seasonal Changes
How is Dengue Fever Diagnosed?
Diagnosing dengue fever involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers assess the patient's symptoms and exposure history to determine the likelihood of infection.
Diagnostic Tests
- NS1 antigen test: Detects the presence of the dengue virus antigen in the blood.
- Serology tests: Measure antibodies against the dengue virus in the blood.
- RT-PCR: Identifies the genetic material of the virus for early detection.
Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for proper management and to prevent complications.
Treating Dengue Fever: What You Need to Know
There is no specific medication to treat dengue fever. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Hospitalization may be required for severe cases.
Management Strategies
- Rest and hydration: Encourage patients to drink plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration.
- Pain relief: Use acetaminophen for fever and pain, avoiding aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Close monitoring: Regularly monitor patients for signs of severe dengue.
Preventing Dengue Fever: Effective Strategies
Preventing dengue fever involves controlling mosquito populations and reducing the risk of bites. Community involvement is key to successful prevention efforts.
Personal Protection
- Use insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and pants, especially during peak mosquito activity.
- Sleep under mosquito nets in areas with high mosquito density.
Environmental Control
- Eliminate standing water in and around homes to reduce mosquito breeding sites.
- Install window and door screens to keep mosquitoes out.
- Use larvicides in areas where mosquito breeding cannot be prevented.
Global Statistics and Trends
According to WHO, the number of dengue cases reported to the organization has increased dramatically over the past few decades. In 2019 alone, more than 5.2 million cases were reported from 100 countries. This trend highlights the urgent need for effective prevention and control measures.
Regions Most Affected
- South-East Asia: India, Thailand, and Indonesia report some of the highest numbers of dengue cases.
- Americas: Brazil and Mexico have seen significant outbreaks in recent years.
- Western Pacific: The Philippines and Vietnam are among the countries with high incidence rates.
The Role of Vaccines in Fighting Dengue
While there is no universal vaccine for dengue fever, several vaccines are currently available or under development. The most widely used vaccine, Dengvaxia, has been approved in over 20 countries for use in individuals aged 9-45 years who have had a previous dengue infection.
Challenges in Vaccine Development
- Variability among the four dengue virus serotypes complicates vaccine development.
- Ensuring safety and efficacy in diverse populations remains a significant challenge.
- Ongoing research aims to develop a single-dose vaccine effective against all serotypes.
The Impact of Dengue Fever on Public Health
Dengue fever poses a significant economic and social burden on affected communities. The cost of healthcare, lost productivity, and strain on healthcare systems can be substantial. In addition, the psychological impact on individuals and families cannot be overlooked.
Economic Costs
- Direct costs include hospitalization, medication, and diagnostic tests.
- Indirect costs involve lost income due to illness and caregiving responsibilities.
Future Directions in Dengue Research
Advancements in technology and scientific understanding offer hope for better prevention and treatment of dengue fever. Research is ongoing in several key areas.
Innovative Approaches
- Genetically modified mosquitoes to suppress populations.
- Wolbachia bacteria to reduce the ability of mosquitoes to transmit the virus.
- Improved diagnostic tools for rapid and accurate detection.
Conclusion
Dengue fever is a complex and challenging disease that requires a multifaceted approach to control and prevent. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and implementing effective prevention strategies, we can reduce its impact on global health. It is essential for individuals, communities, and governments to work together to combat this growing threat.
We encourage readers to share this article and stay informed about the latest developments in dengue fever research. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against this devastating disease. For more information, consult reliable sources such as the World Health Organization or your local health department.