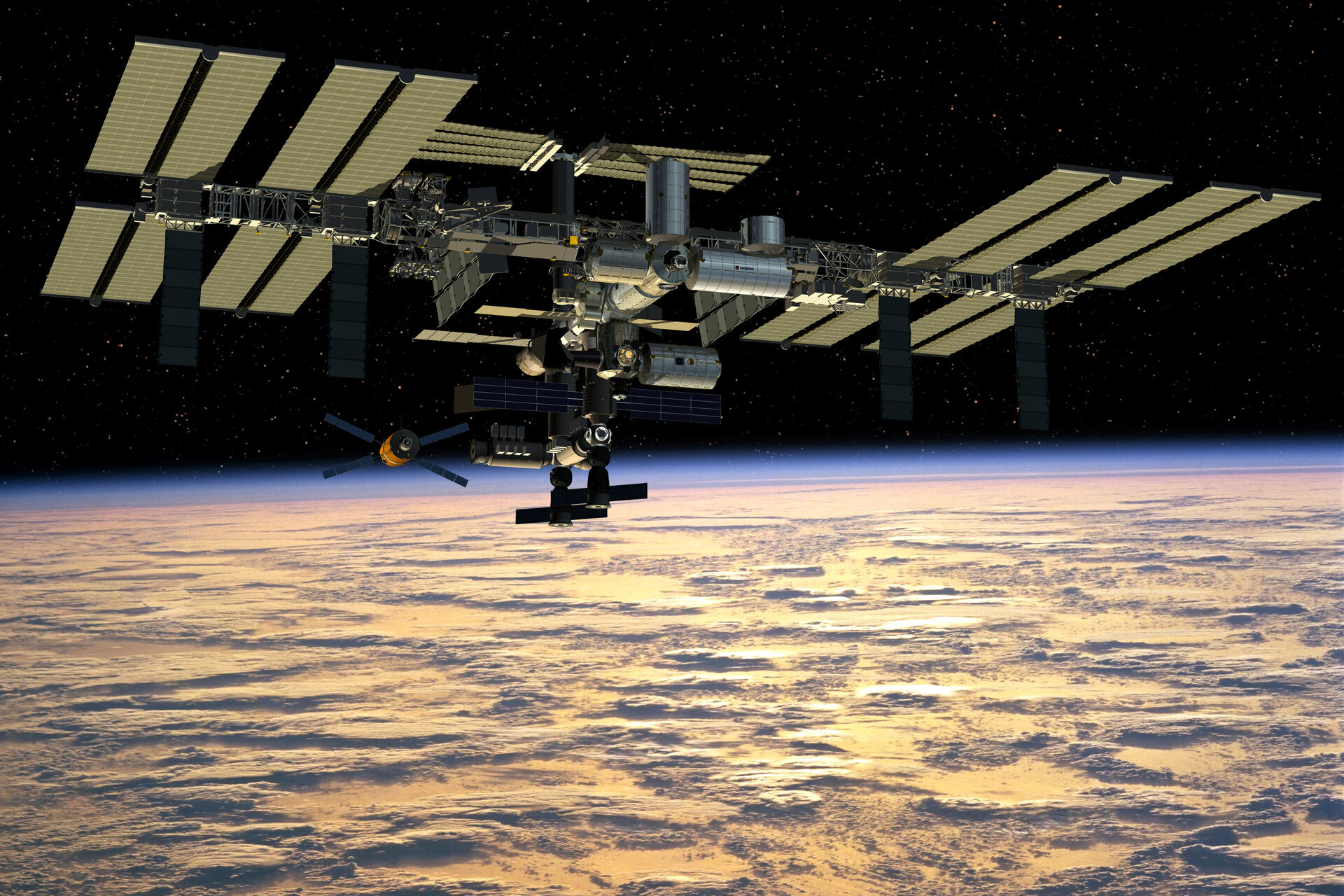
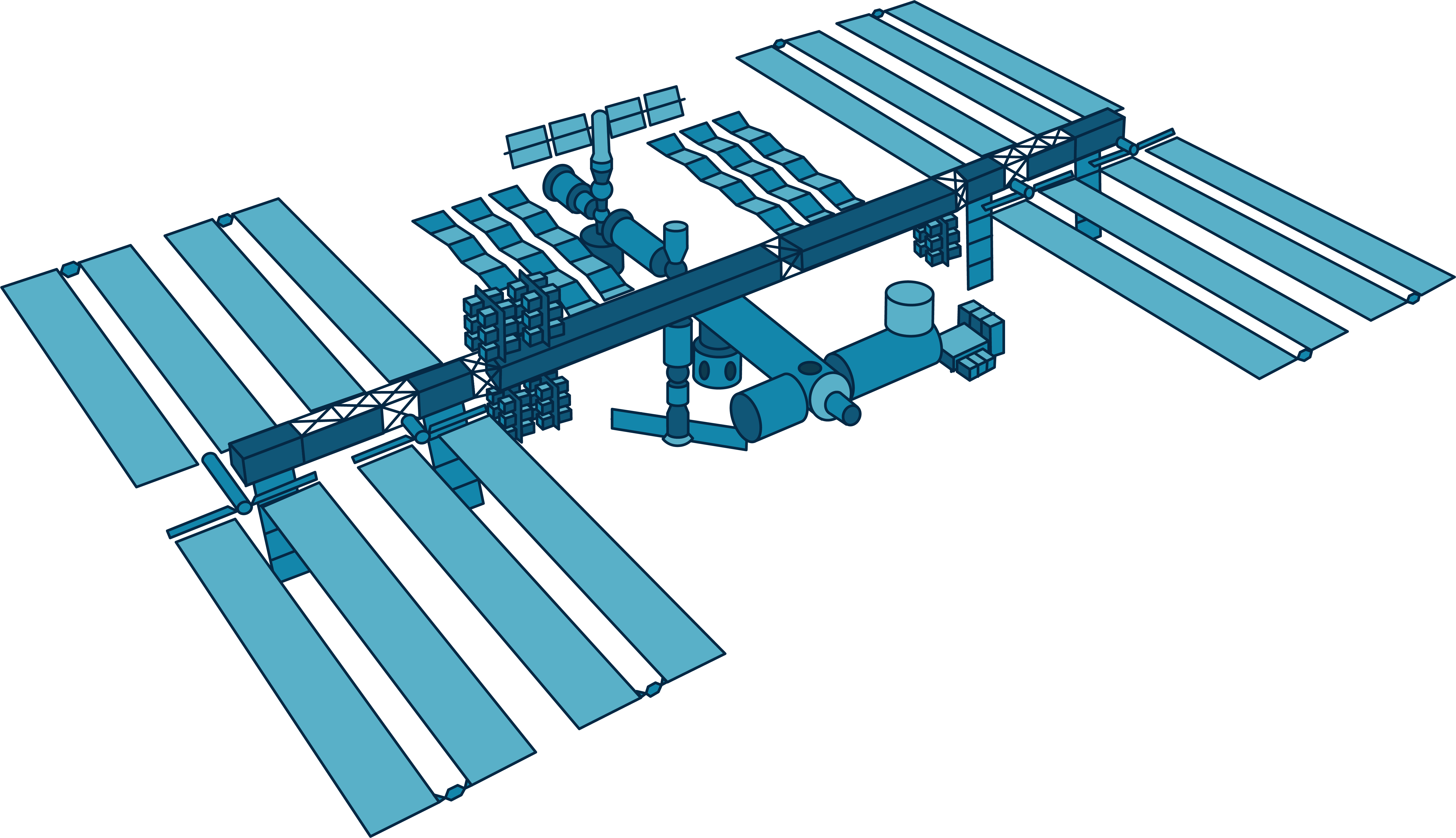
The International Space Station (ISS) represents one of humanity's most ambitious scientific endeavors, serving as a symbol of global collaboration and innovation in space exploration. Orbiting approximately 400 kilometers above Earth, the ISS has become a cornerstone of modern space science, providing unparalleled opportunities for research and discovery. This floating laboratory in space has redefined our understanding of life beyond Earth and continues to inspire generations of scientists, engineers, and dreamers worldwide.
Since its inception, the ISS has been a testament to what can be achieved when nations come together with a shared vision. Launched in 1998 through a partnership between the United States, Russia, Europe, Japan, and Canada, the station has grown into a massive orbiting complex, housing cutting-edge technology and enabling groundbreaking experiments. Its existence is a powerful reminder of the potential for international cooperation in the pursuit of knowledge.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of the International Space Station, this article will explore its history, design, scientific contributions, and future prospects. By understanding the significance of the ISS, we gain insights into the challenges and triumphs of space exploration, as well as the possibilities it holds for the future of humanity. Let us embark on this journey to uncover the marvels of the International Space Station.
Read also:Evenflo Recall A Comprehensive Guide To Ensure Your Babys Safety
Table of Contents
- The History of the International Space Station
- Design and Structure of the ISS
- Scientific Research on the ISS
- Life Aboard the ISS
- Challenges Faced by the ISS
- Benefits of the ISS to Humanity
- International Partnerships
- The Future of the ISS
- Costs and Funding
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The History of the International Space Station
The concept of a space station orbiting Earth dates back to the early days of space exploration. However, it was not until the late 20th century that the idea of an international collaboration began to take shape. In 1998, the first module of the International Space Station, named Zarya, was launched into orbit, marking the beginning of a monumental project.
Over the years, the ISS has evolved from a single module into a sprawling complex, with contributions from multiple countries. Each module added to the station has expanded its capabilities, enabling more advanced experiments and research. The history of the ISS is a story of perseverance, innovation, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
Key Milestones in the Development of the ISS
- 1998: Launch of Zarya, the first module of the ISS.
- 2000: Arrival of the first crew, Expedition 1, marking the beginning of continuous human presence aboard the station.
- 2009: Completion of the U.S. segment of the ISS, enhancing its research capabilities.
- 2021: Expansion of commercial partnerships, paving the way for new opportunities in space exploration.
Design and Structure of the ISS
The International Space Station is an engineering marvel, designed to withstand the harsh conditions of space while providing a safe and functional environment for astronauts. Spanning over 100 meters in length, the station consists of multiple modules, solar arrays, and robotic arms, all working together to support its operations.
Components of the ISS
- Modules: The ISS is composed of several modules, each serving a specific purpose, such as housing crew quarters, laboratories, and storage areas.
- Solar Arrays: These massive panels generate power for the station, converting sunlight into electricity to sustain its systems.
- Robotic Arms: Equipped with advanced robotics, the ISS can perform tasks such as capturing visiting spacecraft and conducting maintenance.
Scientific Research on the ISS
One of the primary purposes of the International Space Station is to serve as a platform for scientific research. The unique environment of microgravity allows scientists to conduct experiments that would be impossible on Earth. From studying the effects of space on the human body to exploring the behavior of materials in zero gravity, the ISS has contributed significantly to our understanding of science and technology.
Examples of Research Conducted on the ISS
- Biological Studies: Research on how microgravity affects living organisms, including plants, animals, and humans.
- Material Science: Investigation of the properties of materials in space, leading to the development of new technologies.
- Earth Observation: Monitoring environmental changes and natural disasters from space to aid in global conservation efforts.
Life Aboard the ISS
Living aboard the International Space Station presents unique challenges and opportunities for astronauts. From daily routines to recreational activities, life in space requires adaptation and innovation. Astronauts must adhere to strict schedules, balancing their time between scientific experiments, maintenance tasks, and personal care.
Challenges of Living in Space
- Microgravity: Adjusting to the absence of gravity affects everything from movement to eating and sleeping.
- Isolation: The psychological impact of being far from Earth and loved ones requires strong mental resilience.
- Resource Management: Efficient use of limited resources, such as water and food, is crucial for survival.
Challenges Faced by the ISS
Despite its successes, the International Space Station faces numerous challenges, both technical and logistical. From equipment malfunctions to the need for continuous funding, maintaining the station requires constant effort and collaboration among its partners.
Read also:Enrique Hernandez The Journey Of A Remarkable Baseball Player
Common Challenges
- Space Debris: The risk of collisions with debris in orbit necessitates careful monitoring and avoidance maneuvers.
- Funding: Securing financial support for the ISS remains a challenge, especially as space agencies explore new missions beyond Earth's orbit.
- Maintenance: Regular upkeep and repairs are essential to ensure the longevity and functionality of the station.
Benefits of the ISS to Humanity
The International Space Station has provided countless benefits to humanity, both directly and indirectly. Its contributions to science, technology, and international relations have had a profound impact on the world. The knowledge gained from research aboard the ISS has led to advancements in medicine, engineering, and environmental science, among other fields.
Impact on Society
- Inspiration: The ISS serves as a source of inspiration for future generations, encouraging interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM).
- Global Cooperation: The station exemplifies the power of international collaboration, fostering trust and understanding among nations.
- Technological Innovation: Discoveries made on the ISS have led to the development of new technologies with applications on Earth.
International Partnerships
The success of the International Space Station is a testament to the power of international cooperation. The partnership between NASA, Roscosmos, ESA, JAXA, and CSA has been instrumental in the station's development and operation. Each agency brings unique expertise and resources to the table, ensuring the continued success of the project.
Roles of Partner Agencies
- NASA: Provides leadership and technical support, contributing significantly to the station's design and operation.
- Roscosmos: Offers launch capabilities and expertise in space station construction and maintenance.
- ESA: Contributes research facilities and modules, enhancing the scientific capabilities of the ISS.
- JAXA: Provides advanced technology and research facilities, expanding the scope of experiments conducted aboard the station.
- CSA: Supplies robotics and specialized equipment, aiding in the station's functionality and efficiency.
The Future of the ISS
As the International Space Station approaches its third decade of operation, questions about its future loom large. While the station is expected to remain operational until at least 2030, discussions are ongoing regarding its long-term sustainability and potential successors. The ISS will continue to play a vital role in advancing space exploration and preparing humanity for missions beyond Earth's orbit.
Possible Future Directions
- Commercialization: Increased involvement from private companies could lead to new opportunities for research and development.
- Deep Space Exploration: Lessons learned from the ISS will inform future missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
- Technological Advancements: Continued innovation in space technology will enhance the capabilities of the ISS and its successors.
Costs and Funding
The construction and operation of the International Space Station have come at a significant cost. Estimated to exceed $100 billion, the project represents one of the most expensive scientific endeavors in history. However, the value of the knowledge gained and the potential for future discoveries far outweigh the financial investment.
Funding Sources
- Government Agencies: Primary funding comes from the partner agencies, with contributions based on agreed-upon percentages.
- Private Sector: Growing involvement from commercial entities offers new avenues for financial support.
- International Contributions: Collaborative efforts among nations ensure the continued viability of the ISS.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
The International Space Station stands as a testament to human ingenuity and the power of international cooperation. From its inception to its current status as a hub of scientific discovery, the ISS has redefined our understanding of space exploration. Its contributions to science, technology, and global relations have had a lasting impact on humanity.
As we look to the future, the ISS will continue to inspire and challenge us, pushing the boundaries of what is possible. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and encourage you to explore other articles on our site for more insights into the wonders of space exploration. Together, we can continue to dream, discover, and achieve the impossible.