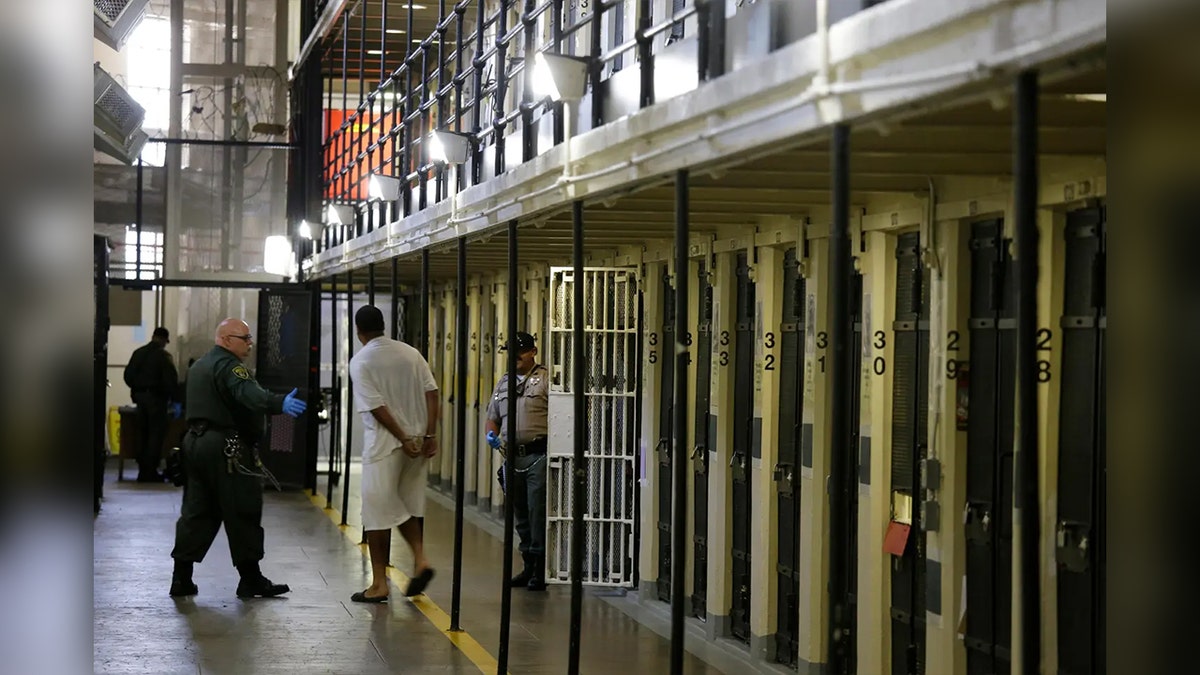
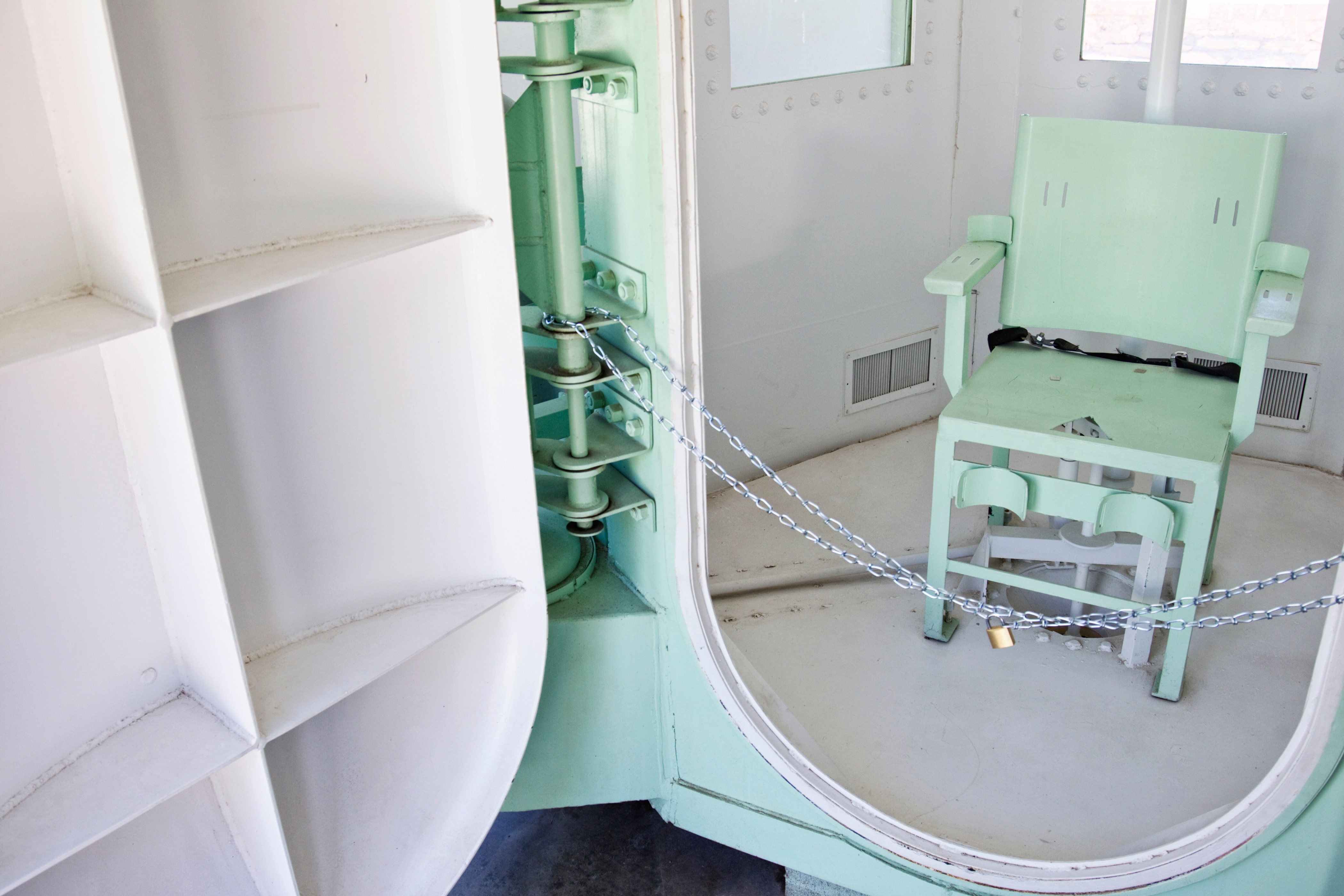
On August 15, 2023, Louisiana became the first state in the United States to use nitrogen gas as a method of execution for death row inmates. This landmark event marks a significant shift in the execution protocols adopted by the state, sparking widespread debates about its ethical implications and effectiveness. The use of nitrogen gas is not only a new chapter in Louisiana's history but also raises crucial questions about the future of capital punishment in America.
The decision to implement nitrogen hypoxia as an alternative method for executions stems from growing concerns over the legality, availability, and humaneness of lethal injection drugs. With pharmaceutical companies increasingly refusing to supply drugs for executions, states like Louisiana are exploring alternative methods that are perceived to be less painful and more humane. However, the effectiveness and legality of nitrogen gas as an execution method remain subjects of intense scrutiny.
This article delves into the details of Louisiana's decision to use nitrogen gas, exploring its historical context, the science behind nitrogen hypoxia, legal challenges, public opinion, and the ethical dilemmas surrounding capital punishment. By analyzing these aspects, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this groundbreaking event and its implications for the future of death row executions.
Read also:Stephanie Soos Husband Everything You Need To Know About His Face And Their Relationship
Table of Contents
- Biography of Key Figures Involved
- History of Execution Methods
- Nitrogen Gas as an Alternative
- Scientific Aspects of Nitrogen Hypoxia
- Legal Considerations and Challenges
- Public Opinion and Societal Impact
- Ethical Dilemmas Surrounding Capital Punishment
- International Perspective on Capital Punishment
- Future of Execution Methods in the U.S.
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Biography of Key Figures Involved
The implementation of nitrogen gas in Louisiana's execution protocols involves several key figures, including lawmakers, legal experts, and corrections officials. Below is a brief overview of the individuals who have played pivotal roles in this decision:
Biographical Information
| Name | Position | Role in Nitrogen Gas Decision |
|---|---|---|
| Governor John Bel Edwards | Governor of Louisiana | Approved the adoption of nitrogen gas as an execution method. |
| Greg Willett | Corrections Commissioner | Oversaw the development and implementation of nitrogen gas protocols. |
| Attorney General Jeff Landry | State Attorney General | Provided legal guidance on the legality of nitrogen gas use. |
History of Execution Methods in the U.S.
Throughout history, the United States has experimented with various methods of execution, each reflecting the societal norms and technological advancements of its time. From hanging to electrocution, gas chambers to lethal injection, the evolution of execution methods has been a controversial journey.
Historically, hanging was the primary method of execution in the U.S. until the late 19th century. The introduction of the electric chair in the late 1800s was marketed as a more humane alternative. However, concerns about botched executions and the inhumane nature of electrocution led to the adoption of lethal injection in the 1980s. Now, with the challenges posed by lethal injection drugs, states like Louisiana are turning to nitrogen gas as the next step in this historical progression.
Key Milestones in Execution Methods
- Hanging – Widely used until the late 19th century.
- Electrocution – Adopted in the late 1800s as a supposedly more humane method.
- Gas Chambers – Used extensively in the mid-20th century but largely abandoned due to safety concerns.
- Lethal Injection – Became the predominant method in the 1980s.
- Nitrogen Gas – Emerging as a new alternative in the 21st century.
Nitrogen Gas as an Alternative Execution Method
Louisiana's decision to adopt nitrogen gas as an execution method is rooted in the need for a more reliable and humane alternative to lethal injection. Nitrogen hypoxia involves the use of nitrogen gas to replace oxygen in the lungs, leading to death by asphyxiation. Advocates argue that this method is less painful and more humane than other forms of execution.
How Nitrogen Hypoxia Works
Nitrogen gas is administered in a controlled environment, gradually replacing oxygen in the air. This process causes the inmate to lose consciousness and eventually die due to lack of oxygen. Unlike lethal injection, nitrogen hypoxia does not require the use of drugs, making it a viable option in the face of pharmaceutical restrictions.
Scientific Aspects of Nitrogen Hypoxia
The science behind nitrogen hypoxia is relatively straightforward. Nitrogen gas is non-toxic and widely available, making it an attractive option for execution protocols. However, the effectiveness and safety of this method have yet to be fully established through rigorous scientific studies.
Read also:Sea Hear Now 2025 The Ultimate Guide To Music Art And Culture Festival
Potential Benefits and Risks
- Benefits: Nitrogen gas is inexpensive, readily available, and does not involve the use of pharmaceuticals.
- Risks: There is limited research on the human experience of nitrogen hypoxia, raising concerns about its effectiveness and potential for suffering.
Legal Considerations and Challenges
The legality of nitrogen gas as an execution method is still under debate. While Louisiana has taken the first step in implementing this method, legal challenges are likely to arise as other states consider adopting similar protocols. The U.S. Constitution's Eighth Amendment prohibits cruel and unusual punishment, and the use of nitrogen gas will undoubtedly be scrutinized under this framework.
Key Legal Questions
- Does nitrogen hypoxia constitute cruel and unusual punishment?
- What are the legal implications of using a method that has not been extensively tested?
Public Opinion and Societal Impact
Public opinion on capital punishment remains divided, with proponents arguing that it serves as a deterrent to crime while opponents claim it is inhumane and ineffective. The introduction of nitrogen gas as an execution method is likely to reignite debates about the morality and effectiveness of capital punishment.
Public Reaction to Nitrogen Gas
Surveys indicate that public opinion is split on the use of nitrogen gas. While some view it as a more humane alternative, others remain skeptical about its ethical implications. The societal impact of this decision will depend on how effectively the state communicates the rationale behind its adoption.
Ethical Dilemmas Surrounding Capital Punishment
Capital punishment raises profound ethical questions about the role of the state in taking a human life. The use of nitrogen gas does not eliminate these dilemmas but rather shifts the focus to the method of execution. Ethical considerations include the potential for wrongful convictions, the fairness of the judicial process, and the moral implications of state-sanctioned executions.
Key Ethical Concerns
- The possibility of executing innocent individuals.
- The fairness and consistency of the judicial system.
International Perspective on Capital Punishment
While the U.S. continues to practice capital punishment, many countries around the world have abolished it. The use of nitrogen gas in Louisiana's execution protocols places the state at odds with global trends toward the abolition of the death penalty. International organizations and human rights groups have criticized the continued use of capital punishment, arguing that it violates fundamental human rights.
Future of Execution Methods in the U.S.
The adoption of nitrogen gas by Louisiana could set a precedent for other states facing similar challenges with lethal injection drugs. However, the future of execution methods in the U.S. remains uncertain, as legal and ethical debates continue to shape the landscape of capital punishment.
Possible Developments
- More states may adopt nitrogen gas as an execution method.
- Further legal challenges could delay or halt the implementation of nitrogen gas.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Louisiana's decision to use nitrogen gas for the first time in a death row execution marks a significant moment in the history of capital punishment in the U.S. While proponents argue that this method is more humane and reliable, critics raise concerns about its ethical implications and effectiveness. The future of execution methods in the U.S. will depend on how these debates unfold and how states navigate the complex legal and ethical landscape of capital punishment.
We invite readers to engage in this conversation by sharing their thoughts and opinions in the comments section below. Your feedback is crucial in shaping the discourse around this critical issue. Additionally, we encourage you to explore other articles on our site that delve into related topics, such as the history of capital punishment and the global movement toward its abolition.
For further reading, consider consulting the following sources: